To effectively budget for your global expansion, you need transparency into how MultiLipi quantifies "work." We don't just count words; we analyze Unique Linguistic Segments. This guide provides a granular breakdown of how our metering engine calculates usage, what is included in that count, and how our Smart Deduplication technology saves you money.
Real-time word count dashboard showing per-language translation metrics
1. The Core Calculation Logic
Your plan utilization is determined by the Total Unique Source Words processed for translation.
The Formula:
[Unique Source Words] × [Number of Target Languages] = Total Usage
The "Multiplier Effect"
Because each language requires a distinct neural translation pass, adding a language acts as a multiplier.
Example Scenario:
Your Homepage: 1,000 words
Ação: You translate it into French and German
Calculation: 1,000 words × 2 languages = 2,000 Total Words Used
2. Smart Deduplication
How We Save You Quota
This is the most critical concept for efficiency.
MultiLipi uses a Memória de Tradução (TM) . We do not charge you for the same sentence twice.
Repeated Content (Headers/Footers):
If your site has a footer with the text "Copyright 2024 All Rights Reserved" that appears on 500 pages, we only count and translate it once. The system identifies the string hash and applies the existing translation to all 500 pages automatically.
Result: You pay for the unique string, not the page views or repetitions.
3. The "Invisible" Layers
What Else is Counted?
Many users are surprised to see a word count higher than their visible paragraph text. This is because MultiLipi translates the entire infrastructure required for SEO, not just the visible UI.
The Metering Engine includes:
Visible UI
Paragraphs, Headlines (H1-H6), Buttons, and Menu Items.
SEO Metadata
- Meta Titles & Descriptions: Critical for click-through rates in Google.
- OpenGraph Tags: Content used when your link is shared on Facebook/LinkedIn.
Accessibility Layers
- Image Alt Text: (
<img alt="...">) Essential for ranking in Google Images and for screen readers. - Placeholders: Input field hints (e.g., "Enter your email...").
- Dynamic Payloads: Text injected via JavaScript (e.g., error messages, pop-ups, notification toasts).
4. Updates & Revisions
The "Diff" Logic
What happens when you edit your website?
Minor Edits:
If you change a single sentence on a 1,000-word page, our engine detects the "Difference." You are only charged for the new sentence (e.g., 15 words), not the re-translation of the entire page.
HTML Restructuring:
If you significantly change the HTML structure wrapping the text, the system may recognize it as a new segment.
5. How to Optimize Your Usage
Strategies to conserve words and maximize efficiency
Exclude "Legalese"
Use the Exclusion Rules to block translation on Terms of Service or Privacy Policy pages, which are often long and legally required to be in English (depending on jurisdiction).
Block User-Generated Content
If you have a comments section or reviews widget, exclude that HTML block from translation to prevent users from eating up your quota.
Audit Your Languages
Remove underperforming languages to instantly stop new words from accumulating for that region.
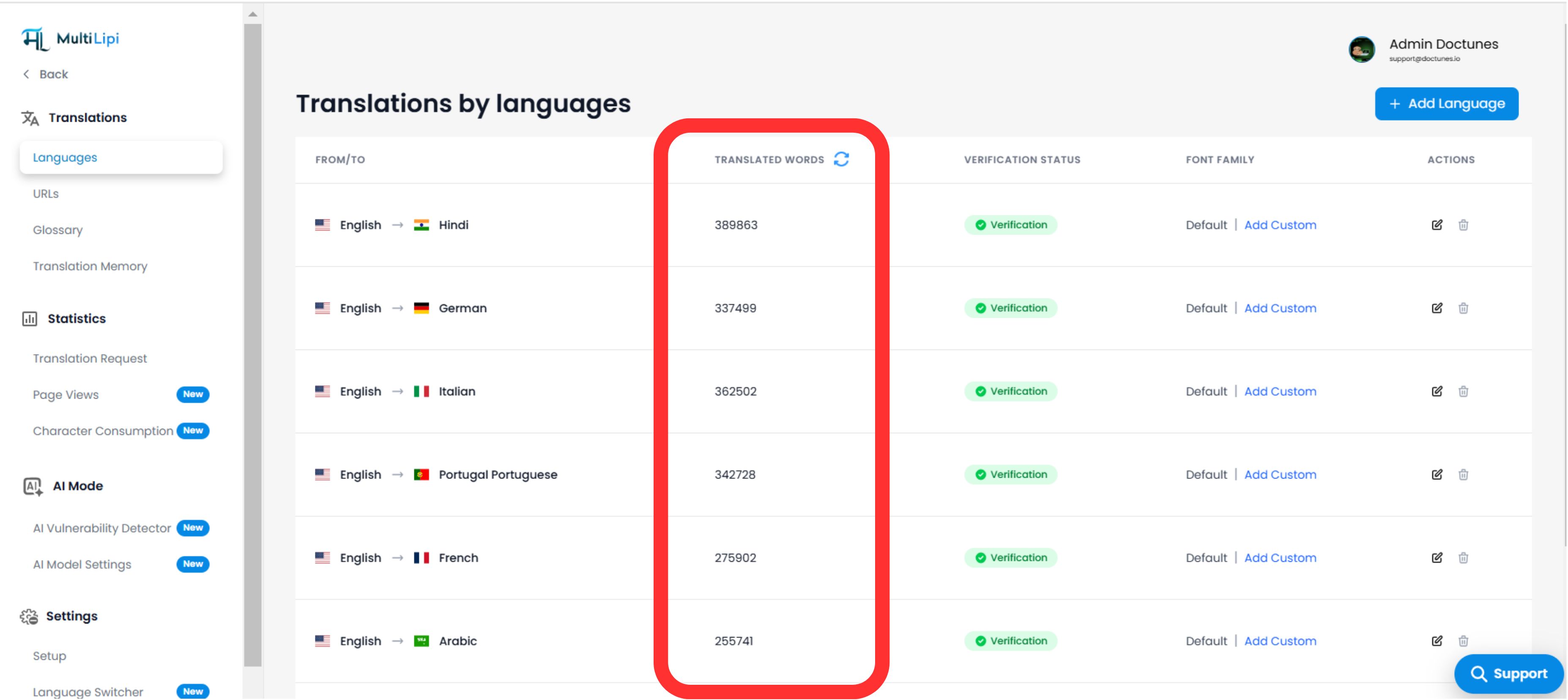
6. Monitoring & Verification
You can audit your consumption in real-time.
Dashboard View:
Navigate to Translations → Languages.
Per-Language Breakdown:
We show the specific count for each language pair (e.g., EN → ES: 14,203 words).
Real-Time Sync:
Click the Refresh Icon 🔄 next to the counter to trigger a live re-calculation of your index.

